How can we use .NET components in COM
What is CCW (COM callable wrapper) ? or How do we ensure that .NET components is compatible with COM ?
✍: Guest
.NET components can not be used in straight forward way with COM. You will need to create CCW in order that COM components communicate with .NET assemblies. Following are the different approaches to implement it :-
ã Explicitly declare interfaces.. Public Interface ICustomer Property CustomerName() As String Property CustomerCode() As String Sub AddCustomer() End Interface Public Class Customer Implements ICustomer Private PstrCustomerName As String Private PstrCustomerCode As String Public Sub AddCustomer() Implements ICustomer.AddCustomer Try e addin of database code can go here Catch ex As Exception Throw ex End Try End Sub Public Property CustomerCode() As String Implements ICustomer.CustomerCode Get Return PstrCustomerCode End Get Set(ByVal value As String) PstrCustomerCode = value End Set End Property Public Property CustomerName() As String Implements ICustomer.CustomerName Get Return PstrCustomerName End Get Set(ByVal value As String) PstrCustomerName = value End Set End Property Public Sub New() End Sub End Class
Note :- Source code of this is provided in CD in SOURCECODE folder in
COMCALLABLEWRAPPER
The above customer class is going to be used by COM components so all the properties and
methods are declared in interface and implemented in the customer class. Customer Name.Customer
Code and AddCustomer are first declared in ICustomer and then implemented in Customer
Class. Also note that the class must have a default constructor.
ã The second way to create CCW is by using InteropServices attributes. Here interfaces
are created automatically.
Following are different type of class attributes :
None:-No class interface is generated for the class. This is default setting when you do not specify
anything.
AutoDispatch :- Interface that supports IDispatch is created for the class. However, no type
information is produced.
AutoDual :- A dual interface is created for the class. Type information is produced and made
available in the type library.
Below in the source code we have used the third attribute.
Imports System.Runtime.InteropServices
<ClassInterfaceAttribute(ClassInterfaceType.AutoDual)> _
Public Class ClsCompliant
End Class
Other than class attributes defined up there are other attributes with which you can govern other
part of assembly.Example “GuidAttribute” allows you to specify the GUID,
“ComVisibleAttribute” can be used to hide .NET types from COM etc. All attributes are not in
scope of the book as this is a interview questions book refer MSDN for more details.
ã Once .NET assembly is created using either interface or using interopservices method
we need to create a COM type library using Type library export tool.
Tlbexp (AssemblyName)
ã The final thing is registering the CCW in registry using regasm tool.
regasm AssemblyName [Options]
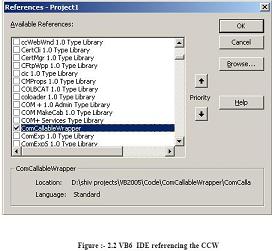
ã Finally refer the TLB in your COM IDE Below is figure showing VB6 IDE referencing
the DLL
Note :- DLL and TLB should be in same directory where the application is executed.
2007-10-22, 6058👍, 0💬