Can you explain different software development life cycles - part II
Can you explain different software development life cycles -part II?
✍: Guest
Water Fall Model
This is the oldest model. It has sequence of stages; output of one stage becomes input of
other.
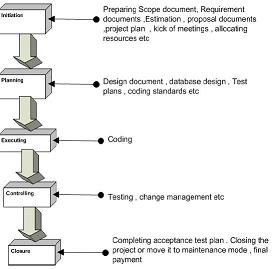
Following are stages in Waterfall model:
System Requirement: - This is initial stage of the project where end user
requirements are gathered and documented.
System Design: - In this stage detail requirements, screen layout, business
rules, process diagram, pseudo code and other documentations are prepared.
This is first step in technical phase.
Implementation: - Depending on the design document actual code is written
here.
Integration and Testing: - All pieces are brought together and tested. Bugs are
removed in this phase.
Acceptance, Installation and Deployment: - This is final stage where software
is put in production and runs actual business.
Maintenance: - This is least glamorous phase which runs forever. Code Changes,
correction, addition etc are done in this phase.
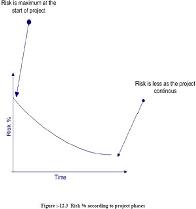
Waterfall is suited for low risk in areas of User Interface and performance requirements,
but high risk in budget and schedule predictability and control. Waterfall assumes that all
requirements can be specified in advance. But unfortunately requirement grows and
changes through various stages, so it needs feedback from one stage to other.
Spiral Model
Spiral Model removes the drawback of waterfall model, by providing emphasis to go
back and reiterate earlier stages a number of times as project progresses. On broader level
it’s a series of short waterfall cycles, each producing an early prototype representing a
part of entire project. It also helps demonstrate a Proof of Concept at early software life
cycle.
Build and Fix Model
This is the way free-lancers work Write some code and keep modifying it until the customer
is happy. This approach can be quite dangerous and risky.
Rapid Prototyping Model
This model is also called as Rapid Application Development. The initial emphasis is on
creating prototype that look and acts like the desired product. Prototype can be created
by using tools which is different from those used for final product. Once the prototype is
approved, its discarded and real software development is started from scratch. The problem
with this model is that sometimes the prototype moves ahead to become the final live
product which can be bad from design point of view. It’s a effective model but can have
higher costing than other models as you require programmers during the initial phase of
the software cycle.
Incremental Model
In this model we divide products into builds, where section of product are created and
tested separately. Here errors are found in requirement phase itself, user feedback is taken
for each stage and code is tested after it is written.
2007-10-30, 6884👍, 0💬