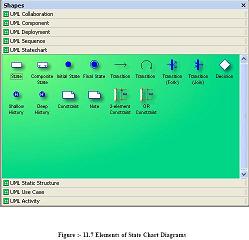
Describe different elements in Static Chart diagrams
Describe different elements in Static Chart diagrams ?
✍: Guest
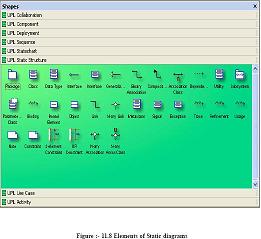
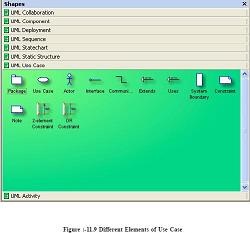
Package: - It logically groups element of a UML model.
Class: - They describe set of objects with similar structure, behavior, and relationships.
Data Type :- A data type is an instance of the DataType metaclass defined in the UML
metamodel. A data type declares a type of class attribute. This type is available as a
string, you can include it when you define attributes for other elements in a model.
Interface :- It specifies the externally operations of a class, component, package, or other
element without specifying internal structure.
Generalization: - It is a relationship between a specific element and a general element,
such that the specific element is fully consistent with the general element and includes
additional information (such as attributes and associations). For example, the classes Car,
Bike, Cycle can all be specific elements of a more general abstract class element named
vehicle.
Binary Association: - It’s a relationship between two classes.
Composition: - A composition is a form of aggregation that indicates that a part may
belong to only one whole and that the lifetime of the whole determines the lifetime of
the part.
Dependency: - Shows relationship between two elements.
Utility : - Whatever Attributes and operations you define for a utility become global
variables and procedures.
Subsystem: - It is a package that contains the contents of the entire system or an entire
model within the system.
Parameterized class: - It is a template that describes a class with one or more unbound
formal parameters.
Binding: - It is a kind of dependency that indicates a binding of parameterized class or
template, parameters to actual values to create a bound, or no parameterized, element.
Bound element : - Parameters of the parameterized class are bound to actual values.
Object: - Represents instance of a class.
Link: - Represents Links between objects.
N-ary Link: - Represents link between an objects.
Meta-Class: - Whose instances are classes.
Signal: - Specifies stimulus between classes for which there is no reply. It is an element
which can be generalized and is defined independently of the classes handling the signal.
Exception: - Signal raised because of bad execution.
Trace: - Indicates historical relationship between two elements.
Refinement: - Refinement is a kind of dependency that indicates a historical or derivation
relationship between two elements with a mapping between them.
Usage : - Usage is a kind of dependency that indicates that one element requires the
presence of another element for its correct implementation or functioning.
2-Element Constraint: - It shows a constraint on two classes or associations.
OR constraint: - It shows an OR constraint on two classes or associations.
2007-10-26, 8114👍, 0💬